
5G technology | disadvantages of 5g | advantages and disadvantages of 5g
5G technology - the new world
CONTENT :
1. How can we define a 5G network?
2. What are the features of 5G technology?
3. How does 5G technology works?
4. Do we need 5G?
5. What are the negatives of 5G technology?
6. How will 5G affect society?
Let's Get Started
5G is the 5th generation mobile network. It is a new global wireless standard after 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G networks. 5G enables a new kind of network that is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together including machines, objects, and devices.
5G wireless technology is meant to deliver higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, ultra-low latency, more reliability, massive network capacity, increased availability, and a more uniform user experience to more users. Higher performance and improved efficiency empower new user experiences and connect new industries.
Like we said, it will represent the next generation of the mobile network, but it will elevate this network in ways that we've never seen before. In fact, in addition to interconnecting devices, it's able to control machines and objects too. It represents a significant evolution in the mobile network, offering multi-Gbps speeds during peak times, low latency, a massive amount of capacity, and a better overall user experience.
2. What are the features of 5G technology?
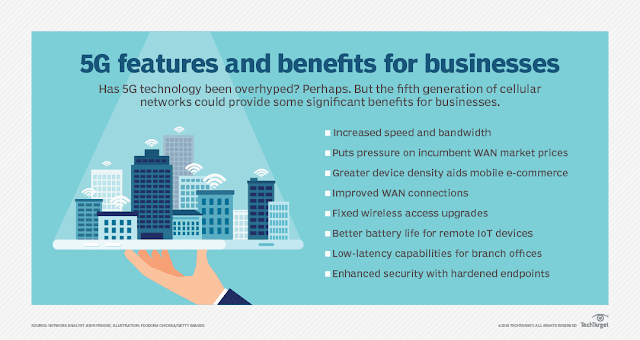
Let's take a closer look at some of the features and benefits of 5G for businesses.
- The most-discussed 5G feature is increased speed and bandwidth. With a data rate of up to 10 Gbps, 5G will bring 10 times to 100 times improvement over the existing 4G LTE technology. Cellular is now a potential technology for branch office automation because WAN connections finally have enough bandwidth. For businesses, the real benefit of 5G might not be the actual bandwidth, but the pressure that 5G exerts on market prices of incumbent WAN connectivity.
- 5G's low latency, as low as 1 millisecond, will be the other key for WAN usage. Customers are using MPLS or dedicated lines today primarily for low latency in line-of-business applications. 5G's low latency may bring additional flexibility that lets businesses jettison some of their branch office MPLS infrastructures in favor of the less expensive and more flexible 5G connections to branches. This is especially true in retail or shared infrastructure or very remote environments.
- 5G density will enable up to 100 times more connected devices in the same physical area that 4G LTE operates today while maintaining 99.999% availability. While this density may bring business advantages for mobile workforces, the real benefit is increasing the size of the mobile customer market. Mobile e-commerce is growing faster than retail and traditional computer-based e-commerce. More customers than ever use mobile technologies to shop online, so greater density increases the overall addressable market.
- An estimated 90% reduction in power consumption for devices means minor power savings at the smartphone level. But, from an infrastructure perspective, especially for IoT devices, the power savings could be significant. Combining IoT devices with a cellular 5G communication means lower power overhead in the design and actual consumption. Remote devices can be expected to last significantly longer when running on battery alone. Some estimates even show that 10-year remote battery life may be achievable for IoT-based sensor devices deployed in remote locations.
- Security is always a concern for mobile devices and IoT devices because the latter lives on the edge of the corporate network. With 5G, stronger security than 4G LTE will be available for designers, including hardware security modules, key management services, over the air, secure elements, and others. This will help ensure that the data transmitted over the 5G network is secure while also hardening network endpoints.
In simple terms:
- Up to 10Gbps data rate - > 10 to 100x speed improvement over 4G and 4.5G networks.
- 1-millisecond latency.
- 1000x bandwidth per unit area.
- Up to 100x number of connected devices per unit area (compared with 4G LTE)
- 99.999% availability.
- 100% coverage.
3. How does 5G technology works?
Wireless communications systems use radio frequencies (also known as a spectrum) to carry information through the air.
5G operates in the same way but uses higher radio frequencies that are less cluttered. This allows for it to carry more information at a much faster rate. These higher bands are called 'millimeter waves' (mmwaves). They were previously unused but have been opened up for licensing by regulators. They had been largely untouched by the public as the equipment to use them was largely inaccessible and expensive.
While higher bands are faster at carrying information, there can be problems with sending over large distances. They are easily blocked by physical objects such as trees and buildings. In order to circumvent this challenge, 5G will utilize multiple input and output antennae to boost signals and capacity across the wireless network.
The technology will also use smaller transmitters. Placed on buildings and street furniture, as opposed to using single stand-alone masts. Current estimates say that 5G will be able to support up to 1,000 more devices per meter than 4G.
5G technology will also be able to ‘slice’ a physical network into multiple virtual networks. This means that operators will be able to deliver the right slice of network, depending on how it is being used, and thereby better manage their networks. This means, for example, that an operator will be able to use different slice capacities depending on importance. So, a single user streaming a video would use a different slice to a business, while simpler devices could be separated from more complex and demanding applications, such as controlling autonomous vehicles.
There are also plans to allow businesses to rent their own isolated and insulated network slice in order to separate them from competing Internet traffic.
90% reduction in network energy usage.
Most operators will initially integrate 5G networks with existing 4G networks to provide a continuous connection.
5G network architecture illustrating 5G and 4G working together, with central and local servers providing faster content to users and low latency applications.
A mobile network has two main components, the ‘Radio Access Network’ and the ‘Core Network’.
- The Radio Access Network - consists of various types of facilities including small cells, towers, masts, and dedicated in-building and home systems that connect mobile users and wireless devices to the main core network.
Small cells will be a major feature of 5G networks, particularly at the new millimeter wave (mmWave) frequencies where the connection range is very short. To provide a continuous connection, small cells will be distributed in clusters depending on where users require a connection which will complement the macro network that provides wide-area coverage.
5G Macro Cells will use MIMO (multiple input, multiple outputs) antennas that have multiple elements or connections to send and receive more data simultaneously. The benefit to users is that more people can simultaneously connect to the network and maintain high throughput. Where MIMO antennas use very large numbers of antenna elements they are often referred to as ‘massive MIMO’, however, the physical size is similar to existing 3G and 4G base station antennas.
- The Core Network - is the mobile exchange and data network that manages all of the mobile voice, data, and internet connections. For 5G, the ‘core network’ is being redesigned to better integrate with the internet and cloud-based services and also includes distributed servers across the network improving response times (reducing latency).
Many of the advanced features of 5G including network function virtualization and network slicing for different applications and services, will be managed in the core. The following illustration shows examples of local cloud servers providing faster content to users (movie streaming) and low latency applications for vehicle collision avoidance systems.
Example of a local server in a 5G network providing faster connection and lower response times
Network Slicing – enables a smart way to segment the network for a particular industry, business, or application. For example, emergency services could operate on a network slice independently from other users.
Network Function Virtualization (NVF) - is the ability to instantiate network functions in real-time at any desired location within the operator’s cloud platform. Network functions that used to run on dedicated hardware for example a firewall and encryption at business premises can now operate on software on a virtual machine. NVF is crucial to enable the speed efficiency and agility to support new business applications and is an important technology for a 5G ready core.
- Improving accessibility
- Extending the reach of mobile broadband
- Improving safety, health, and security
While many of the applications for 5G are expected to directly impact how businesses run, the implications for accessibility, the reach of mobile broadband, and the improvements in society’s safety, health, and security have the potential to be farther reaching. 5G technology is important for consumers as well as businesses as we move into the Fourth Industrial Revolution and explore all that 5G has to offer, including things we likely have not thought of yet.
4. Do we need 5G?
5G is not only important because it has the potential to support millions of devices at ultrafast speeds, but also because it has the potential to transform the lives of people around the world.
5G also works on the radio frequencies, like 4G smartphones, Wi-Fi networks, and satellite communications. However, the scope of 5G technology goes far beyond 4G. Imagine downloading an HD movie video on the smartphone in just a few seconds, even when many phones are connected to the same hotspot. The lag-free execution and managing things in real-time are highly promising with a 5G network. Such a higher-end network facility will compel enterprises to launch new application technologies compatible with 5G.
Compared to the previous wireless technologies, 5G provides higher data rates, reduced latency, higher capacity systems, energy savings, and cost reductions, making it faster and better than the other wireless technologies.
5. What are the negatives of 5G technology?
- Limited global coverage
- Decreased broadcast distance
- Upload speeds
Weakened device batteries
Phones that use a 5G connection will result in a huge battery drain that reduces the lifespan to a large extent. Hence, manufacturers need to invest in new battery technologies to protect the battery from damages and other problems.
- Cybersecurity
- Lack of encryption early in the connection process
- OBSTRUCTIONS CAN IMPACT CONNECTIVITY
- INITIAL COSTS FOR ROLLOUT ARE HIGH
- LIMITATIONS OF RURAL ACCESS
- BATTERY DRAIN ON DEVICES
- UPLOAD SPEEDS DON’T MATCH DOWNLOAD SPEEDS
The range of 5G connectivity is not great as the frequency waves are only able to travel a short distance. Added to this setback is the fact that 5G frequency is interrupted by physical obstructions such as trees, towers, walls, and buildings. The obtrusions will either block, disrupt or absorb the high-frequency signals. To counter this setback, the telecom industry is extending existing cell towers to increase the broadcast distance.
The costs related to the development of 5G infrastructure or adaptations to existing cellular infrastructure will be high. This amount will be further compounded by the ongoing maintenance costs needed to ensure high-speed connectivity, and it’s likely the customers will bear the brunt of these big price tags. Cellular operators are looking to minimize these costs by exploring alternative options in the form of network sharing.
While 5G might bring about real connectivity for the predominantly urban areas, those living in rural settings will not necessarily benefit from the connection. As it stands, many remote areas countrywide are not able to access any form of cellular connectivity. The 5G carriers are going to target big cities with larger populations, eventually working their way into the outer areas, but it’s not likely this will be happening any time soon. As a result, only some of the population will benefit from 5G communication.
When it comes to cellular devices connected to 5G, it seems the batteries are not able to operate for a significant period of time. The battery technology needs to advance to allow for this enhanced connectivity, where a single charge will power a cellphone for a full day. Alongside depleted batteries, users are reporting that cellphones are getting increasingly hot when operating on 5G.
The download speeds of 5G technology are incredibly high, in some cases up to 1.9Gbps. However, the upload speeds are rarely more than 100Mbps, which is not quite as incredible as initially touted. In relation to existing mobile connectivity, however, the upload speeds are higher than being seen with 4G LTE.
6. How will 5G affect society?
The positive impact of the Fourth Industrial Revolution and its related emerging technologies will be fully realized through the wide-scale deployment of 5G communication networks in combination with other connectivity solutions. The key functional drivers of 5G will unlock a broad range of opportunities, including the optimization of service delivery, decision-making, and end-user experience. This will result in $13.2 trillion in global economic value by 2035, generating 22.3 million jobs in the 5G global value chain alone.
To better understand how to realize this large estimated economic output potential, PwC collaborated with the World Economic Forum on a new report, which proposes a bottom-up approach analyzing 40 use cases that identified key industrial advances and social impact areas in addition to the main functional drivers of 5G and the required maturity levels of these drivers. Additionally, it maps the 5G ecosystem to identify its components, its stakeholders and interdependencies, and the actions needed to accelerate 5G deployment and fully realize the potential.
At the macro level, the study points to a largely positive impact. The economic output of these six countries is expected to benefit from an estimated €416 billion boost by 2030, thanks to 5G technology. The new networks will result in over 1 million jobs being created. In terms of the environment, 5G technology will prevent 33 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent from being released into the atmosphere.
Aside from the numbers, 5G has many uses that reflect its value as a state-of-the-art technological enabler that can support the general public, communities, and businesses in addressing their challenges. “5G will have even more uses than 4G,” Roberts adds. “While 4G belonged to the generation of smartphone technology, 5G will belong to that generation and to the generation of smart factories, smart buildings, smart cities and so on. It will contribute to the creation of businesses and jobs in numerous sectors and improve the efficiency of existing industries. The new networks will also tie in closely with the environmental strategies that countries implement. As an example, Poland hopes to gradually increase the share of renewables in its energy mix, even though its energy needs and economy are still largely reliant on coal. 5G could help ease this transition in different ways, by connecting solar/wind farms to optimise how they are managed, maintained and more.”
Research work for use by the entire ecosystem
While this study provides valuable insight into countries with a stake in the potential benefits of 5G where Orange operates, it is also meant for use by the ecosystem as a whole. “The report gives countries an indication as to where 5G will be most effective, enabling them to better focus their efforts and investments,” says Karine Dussert-Sarthe. Going further, we are looking to make it an open, publicly accessible source of information, with the aim of enhancing understanding of the impacts of 5G amongst all players in the ecosystem and ultimately encouraging widespread adoption of the technology. In a way, this study stands as a call for action for everyone to embrace 5G. The torch now passes to Orange 5G Labs, who can enable businesses and communities to test this technology’s real-world potential and devise its use cases for tomorrow.”
“The impacts of 5G are being felt today and will continue to grow,” says Mike Roberts in summary. “It can be a powerful force in supporting the economy, the jobs market and reductions in greenhouse gas emissions that are set out in the study. We are not saying that the technology is perfect—there are pros and cons—but the positives outweigh the negatives on the whole.”










0 Comments:
If you have any promblem, please let me know!